[ad_1]
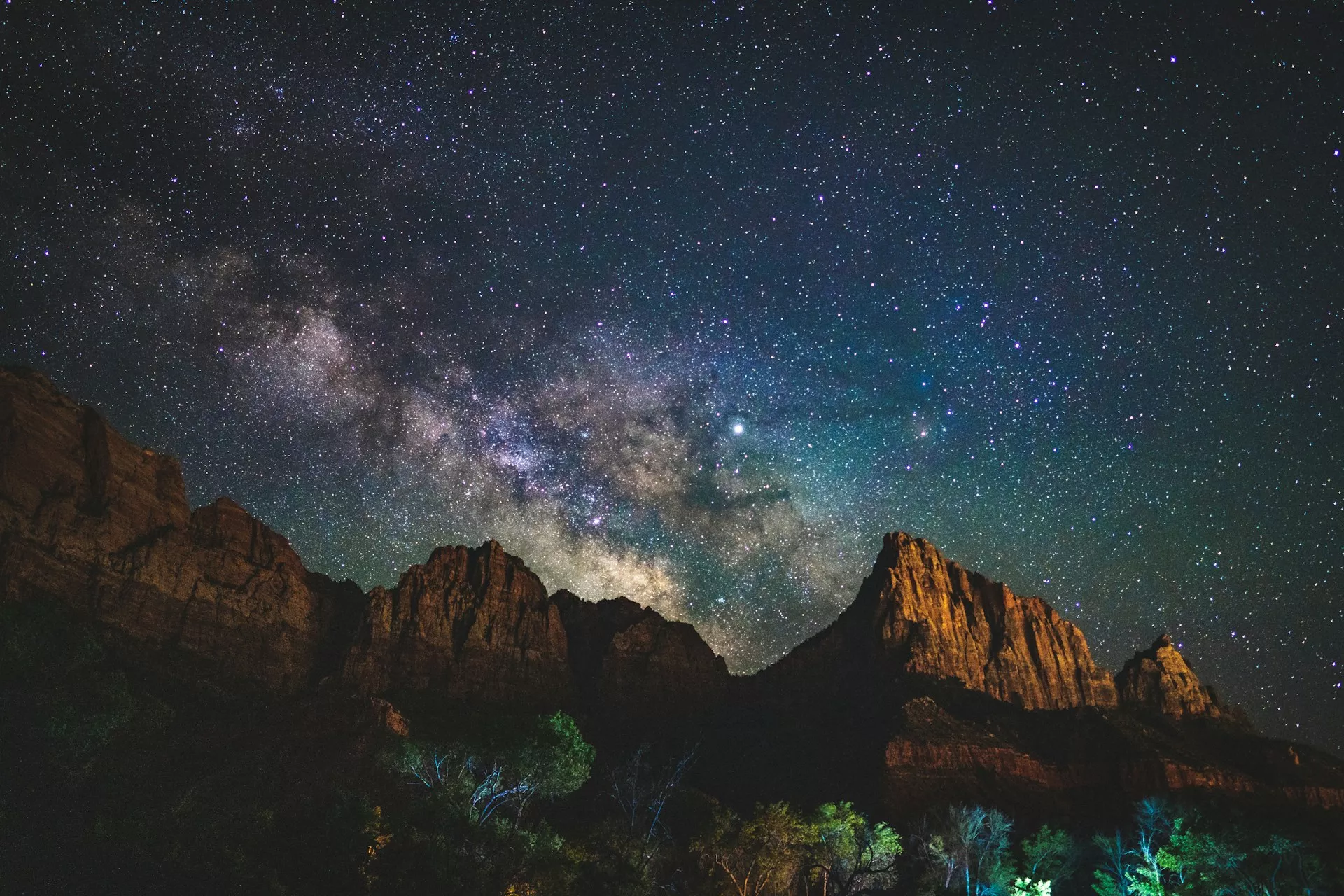
Night sky is an addictive subject to photograph and if you look closer, there are many night sky objects that you can photograph, other than the moon and the Milky Way. On very clear nights, you will be able to see a lot of nebulae, star clusters, cloud complexes and even a galaxy without the aid of a telescope.
Right now it is the Milky Way season in the Northern Hemisphere, but for those who live in the Southern Hemisphere, there are many objects in the Winter sky that are worth photographing. If you are new to astrophotography, start by photographing the moon and then move on to photograph the Milky Way, before working towards photographing deep space objects.
Grab your Milky Way Photography Blueprint for free right here.
In this article here, we have put together a collection of tutorials that are highly detailed and provide you with every information you need to photograph the sky at night. Don’t forget to check out the “Further Reading” section.
Let us start with the Moon which is the natural satellite to our planet Earth and it is one of the closest and brightest subjects in the night sky, that you can easily photograph. If you observe the moon over a few weeks, you will get an understanding of the phases of the moon, its rising and setting time, etc. You just need to do a little bit of planning to get the best shot.
If you are wondering what if you do not have a camera yet, but only a smartphone that you use to capture photos right now? Smartphone technology has advanced quite a lot in the recent years and they can be used to capture beautiful images of the moon and some brighter objects in the night sky. Especially if you are a a beginner in astrophotography, with some practice and knowledge, you can capture interesting photos of the moon with your smartphone.
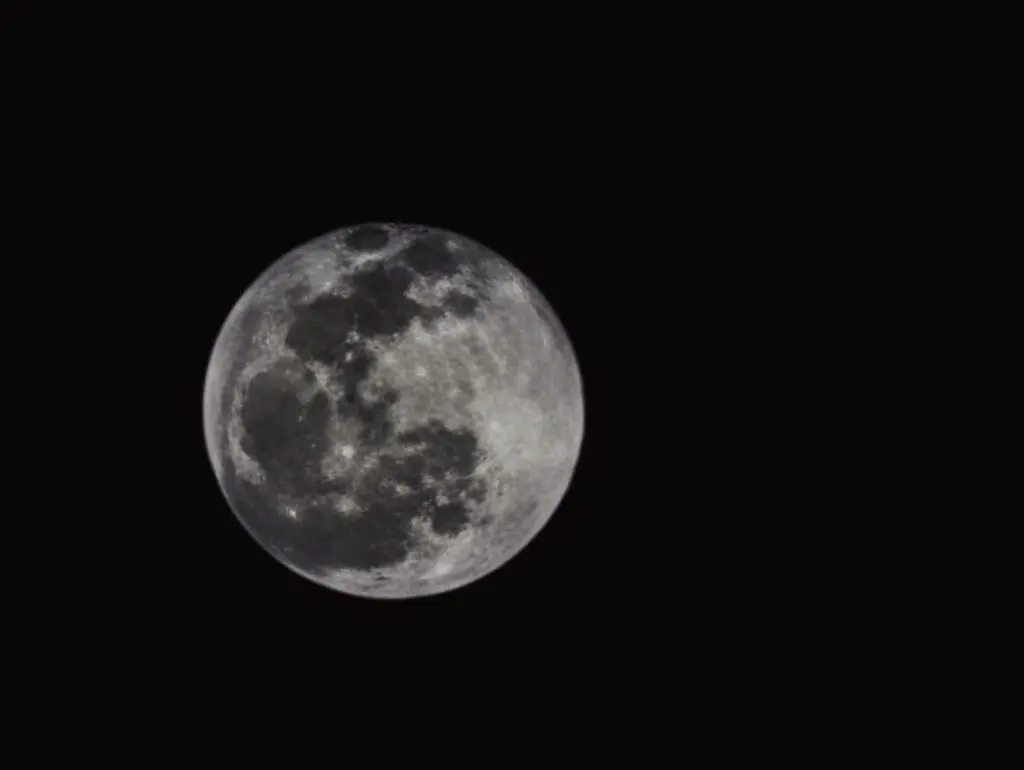

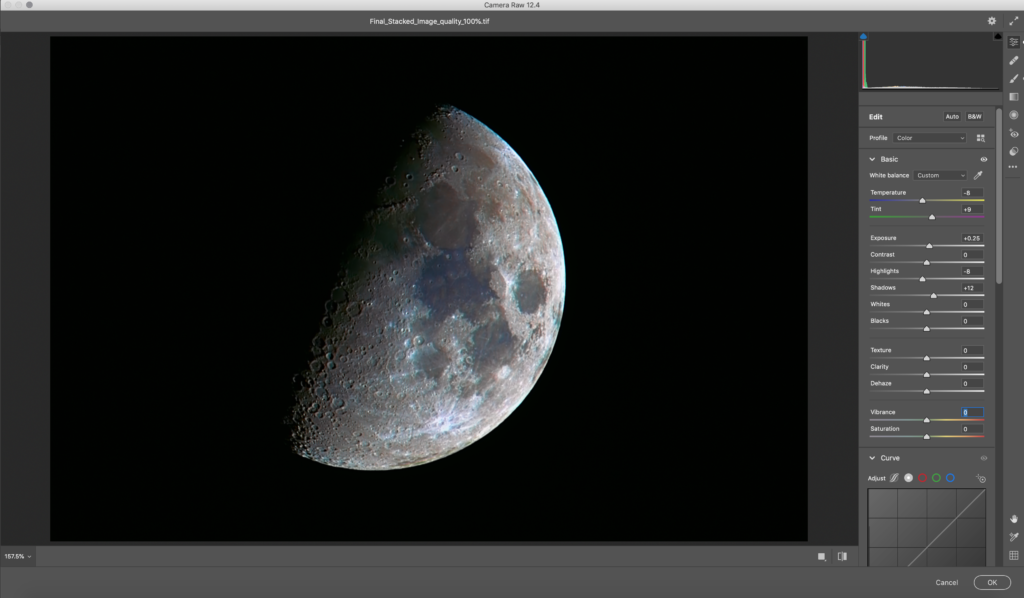
And, did you know that the moon is not just white, but has some colours due to the mineral deposits on its surface? If you zoom in on live view with a long lens, on a very clear night, you will be able to observe these colours faintly. You can photograph the moon and bring in those beautiful colours and this article will help you achieve that. It is interesting and can be done during any phase of the moon, but remember that you will have to take a series of shots to get the best results in terms of colours and details.
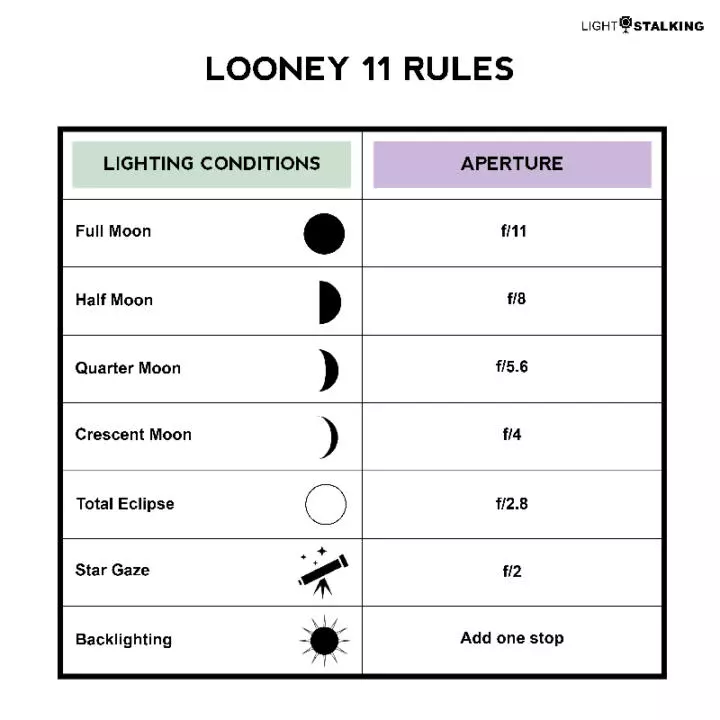
We have heard of rules for correctly setting exposure for certain subjects in photography, rules that do not need to be followed as such, but rules that can help you get started initially and then can be refined further according to the situation. One such rule to capture the moon is the Looney 11 rule which can be a start to estimate exposure times. We will summarise the rule here:
- Set aperture to f/11 and shutter speed to the reciprocal value of ISO.
Check out the article to learn more about this rule.
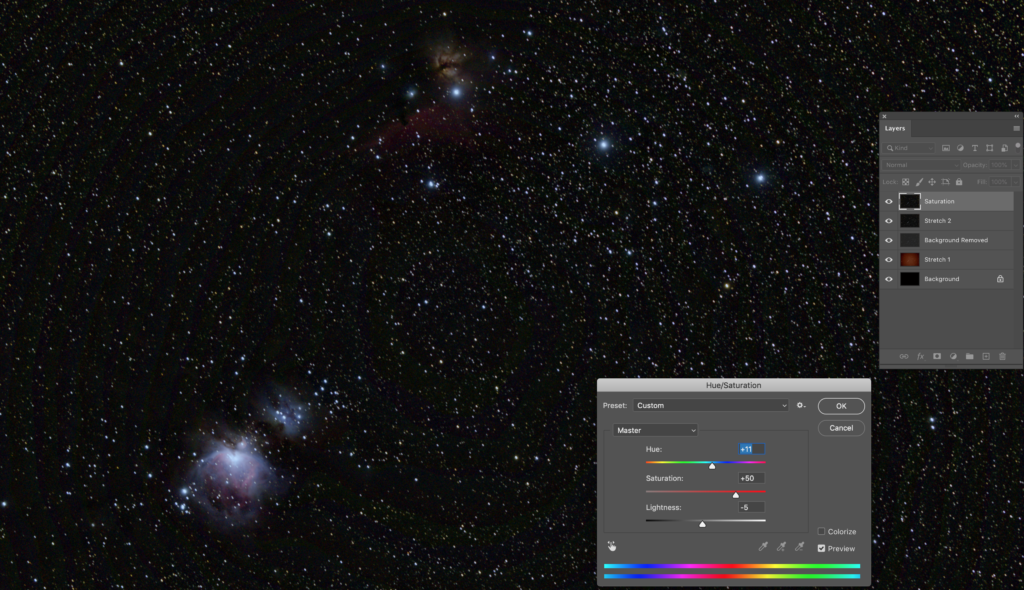
We live in the Milky Way galaxy and it is one of the easiest subjects to photograph, after the moon. Depending on the time of the year, you will be able to photograph only specific areas of the Milky Way galaxy. The core is the most stunning region and it is above the horizon at night, a few months every year. So keep an eye on the weather forecast and find the darkest location possible and photograph the Milky Way with the camera you have in hand.

If you want to go a bit further after some experience and photograph a nebula, the Orion Nebula is one of the easiest to capture and one that is most commonly photographed too. You can use the camera that you have in hand and a moderate focal length lens to capture the frames and then with some detailed post processing, you will have a beautiful image. You will need to capture a series of shots including calibration frames and everything is explained in detail in this article.
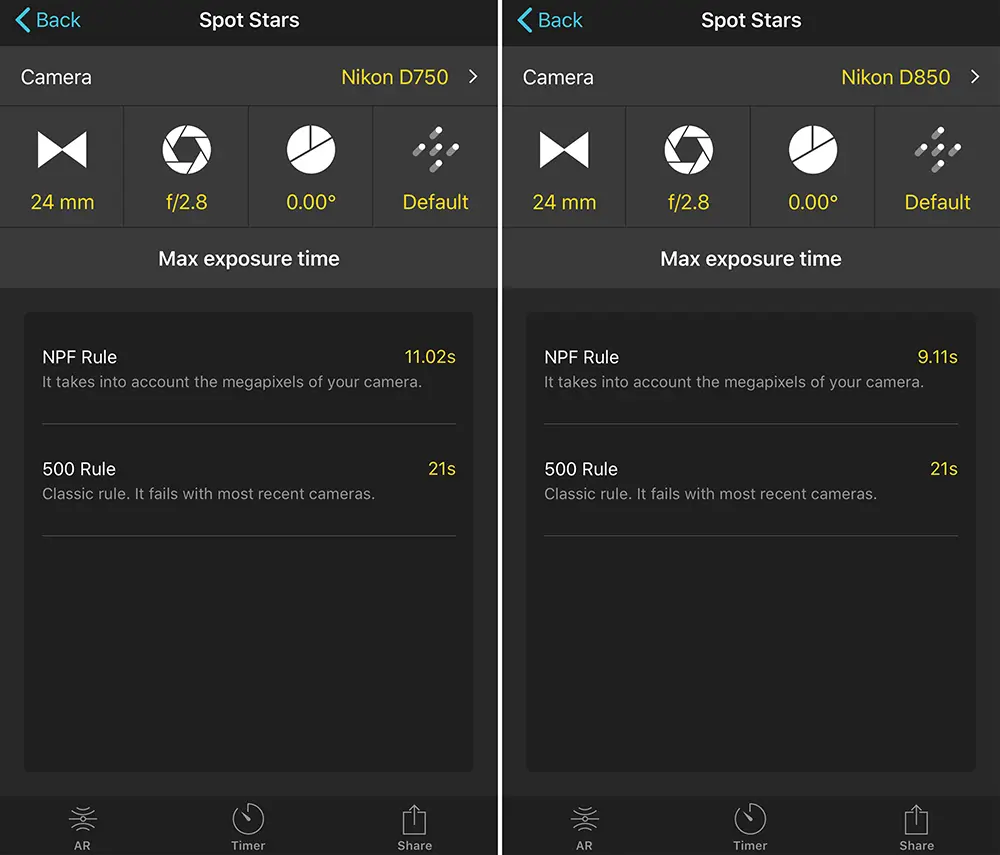
Now, similar to the rule we mentioned above to set exposure for moon photography, if you are a beginner and not sure where to start in terms of settings for your night sky photography like stars, nebulae, etc., start with the 500 rule. It is not very accurate, but is a great start to get an image of the stars, galaxies and the Milky Way. Here is the rule summarised below:
- Set your camera to ISO 3200 or 6400, your Aperture to f/2.8 (or as wide as possible) and your shutter speed to 500 divided by the focal length of your camera, taking into account the crop factor of your camera.
There is also a 600 rule where you replace the 500 above with 600 and see if it works better than the above setting.

With more advanced cameras and sensors, sometimes the 500 or 600 rule may not get you the best results, especially if you want to have a large print. Sometimes there may be some trailing in the stars instead of point sharp stars. To avoid this situation, the photographer needs to calculate exposure based on the type of camera and lens combination.
A formula was devised by Frédéric Michaud for the Société Astronòmique du Havre called the NPF rule which is quite complex, where
- N stands for aperture, the letter N is used to represent aperture in optics.
- P for photosites or pixel density or pixel pitch (distance between two pixels)
- F for focal length
If you have an app called PhotoPills, you can easily calculate exposure times using the NPF rule on that app.
Star photography is easy, but in order to get the best results like sharp and noise free images, there are a few things that you will need to keep in mind. It also requires you to choose the right location, weather conditions, keep an eye on the moon phases and use the right tools and accessories to get the best shot. Last but not the least, patience and practice is key to perfect star images.

Cameras come with noise reduction features called high iso noise reduction and long exposure noise reduction. Many photographers seem to be confused if they need to leave these settings on for astrophotography, in order to get the best results. Depending on what you are shooting, these features can cause some delay in sequences, can cause heat, and also remove faint star details. Read to find if you should leave these settings on or off for astrophotography and why.

When capturing night sky or dep space object, you are working with very little light and longer exposure times. Factors like heat due to long exposure and high iso can induce thermal and/or digital noise in these photographs that can leave unwanted effects/artifacts in the images that also greatly reduce the sharpness and quality of the image. Here are some ways in which noise can be reduced in your night sky images.

Further Reading
[ad_2]
Source link




